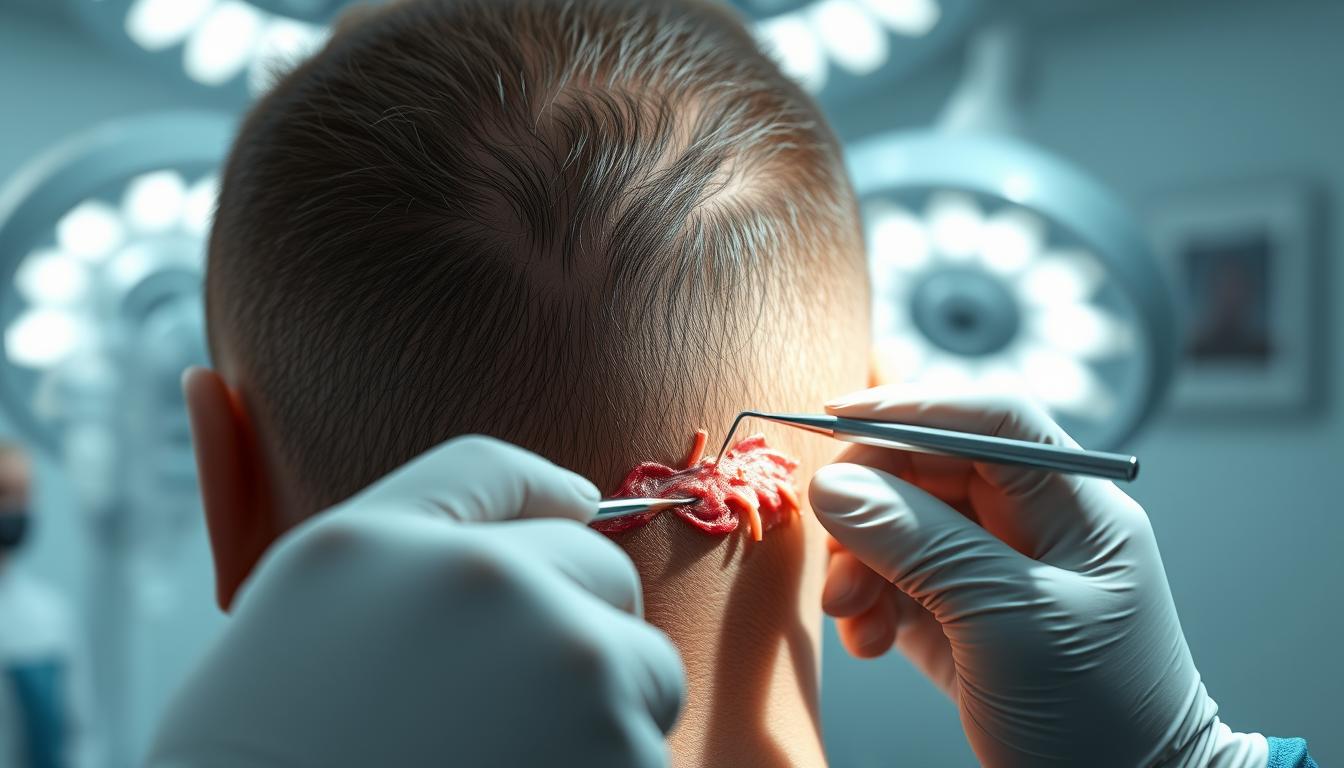
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to address hair loss by relocating hair follicles from donor areas to balding or thinning regions.
Since its inception in the 1950s, hair transplants have evolved significantly, offering more natural-looking results. The procedure involves taking hair from thicker parts of the scalp and grafting it to areas experiencing thinning or baldness.
Understanding hair transplants is essential for anyone considering this surgery as a solution for their hair loss concerns. This article will provide a comprehensive breakdown of the transplant process.
Key Takeaways
- Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure to address hair loss.
- Modern hair transplants offer more natural-looking results.
- The procedure involves relocating hair follicles from donor areas.
- Hair transplants are considered a permanent solution for hair loss.
- Success rates range from 10% to 80% of transplanted hair fully growing back.
Understanding Hair Transplantation
Understanding the intricacies of hair transplantation is crucial for those considering the procedure. Hair transplantation is a surgical technique that has evolved to offer a reliable solution for hair loss.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that relocates hair follicles from a donor site, typically the back or sides of the head, to a recipient site, which is usually the balding or thinning areas. This technique is designed to provide a permanent solution for hair loss, addressing conditions such as male pattern baldness and other forms of alopecia.
History and Evolution of Hair Transplant Techniques
The first hair transplant was performed in 1939 in Japan using single scalp hairs. Over the decades, techniques have evolved significantly. Initially, the “plug” technique was developed, involving the transplantation of large tufts of hair. Modern techniques now utilize mini- and micro-grafts to achieve more natural-looking results.
| Technique | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Plug Technique | Transplanting large tufts of hair | Less natural appearance |
| Mini-grafts | Transplanting smaller groups of hair | Improved natural appearance |
| Micro-grafts | Transplanting individual or small groups of hair | Most natural appearance |
Hair transplantation techniques have advanced to focus on creating natural-looking hairlines and density patterns that match the patient’s original hair growth. These procedures are primarily used to address androgenetic alopecia but can also treat hair loss resulting from scarring or injury.
How Does Hair Transplant Work
A hair transplant involves extracting hair follicles from a donor area and transplanting them to a recipient area. This surgical procedure relies on the principle that hair follicles from the back and sides of the scalp are genetically resistant to balding.
The Basic Principle Behind Hair Transplantation
The fundamental principle behind hair transplantation is the relocation of DHT-resistant hair follicles from permanent donor areas to balding regions affected by pattern hair loss. This ensures that the transplanted hair will continue to grow in its new location.
Donor and Recipient Areas
Donor areas, typically the back and sides of the head, are selected based on their genetic resistance to hair loss. The recipient areas are prepared to receive the transplanted follicles, with considerations for creating a natural hairline and appropriate density.

The Harvesting and Implantation Process
The harvesting process involves extracting hair follicles either individually or in strips, depending on the chosen technique. The implantation process includes creating tiny incisions in the recipient area and carefully placing each graft to ensure proper angle, direction, and density. The transplanted follicles then establish a blood supply in their new location and begin the growth cycle after the procedure.
The success of the procedure depends on the careful handling of follicles during both harvesting and implantation to ensure their viability.
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures
Hair transplant procedures are diverse, but they are mainly classified into two main categories: Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS/FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). These techniques have revolutionized the field of hair restoration, offering patients effective solutions for hair loss.
Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS/FUT)
FUSS involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, typically from the back of the head. The removed strip is then dissected into individual follicular units, which are subsequently transplanted into the recipient areas. This technique allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more modern technique where individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using a micro-punch tool. This method eliminates the need for removing a strip of scalp, resulting in less invasive surgery. The extracted follicles are then implanted into the balding areas.
FUSS vs. FUE: Comparing the Techniques
The primary difference between FUSS and FUE lies in the harvesting method and the resulting scarring. FUSS leaves a linear scar, whereas FUE results in multiple tiny dot scars that are generally less noticeable. Recovery time also varies; FUE typically allows for quicker healing and less post-operative discomfort compared to FUSS. The choice between the two techniques depends on factors such as the patient’s hair characteristics, extent of hair loss, and personal preferences regarding recovery time and scarring.
Variations of these techniques, such as NeoGraft, an automated form of FUE, are also emerging, providing more options for patients. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most appropriate hair transplant procedure.
Step-by-Step Hair Transplant Procedure
The process of hair transplantation involves several key stages, including preparation, harvesting, and implantation. Understanding these steps can help individuals prepare for what to expect during the procedure.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before undergoing a hair transplant, patients must undergo a comprehensive pre-procedure preparation process. This includes an initial consultation with the surgeon to discuss expectations and assess suitability for the procedure. A medical evaluation is also conducted to ensure the patient’s overall health is suitable for surgery. Specific instructions are provided for the days leading up to the surgery, such as avoiding certain medications, alcohol, and smoking.
The Harvesting Phase
The harvesting phase involves removing donor tissue from the scalp. For Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS/FUT), a strip of scalp is removed, and individual follicular units are prepared for transplantation. In Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), individual follicles are extracted directly from the donor area.
The Implantation Phase
During the implantation phase, the surgeon creates recipient sites with precise angles and directions to match natural hair growth patterns. Each graft is then carefully placed into these sites, ensuring proper graft placement density for natural-looking results.
Completing the Procedure
The final steps involve cleaning the surgical areas, applying necessary dressings, and providing immediate post-operative care instructions. The entire procedure typically takes between 4-8 hours, depending on the extent of the transplant.
Ideal Candidates for Hair Transplantation
Hair transplant surgery is not for everyone; certain conditions and characteristics make a person a suitable candidate. The ideal candidate for hair transplantation is someone who has the common form of hair loss known as androgenetic alopecia.
Hair Loss Patterns Suitable for Transplantation
Individuals with male or female pattern baldness who have stabilized hair loss and sufficient donor hair are ideal candidates. The Norwood and Ludwig scales are used to classify the extent of hair loss in men and women, respectively. Hair transplantation is most effective for those with a clear pattern of baldness.
Who Should Avoid Hair Transplants
Those with diffuse unpatterned alopecia, active autoimmune hair loss conditions like alopecia areata, or unrealistic expectations about outcomes should avoid hair transplants. Younger patients (under 25) are often advised to delay transplantation until their hair loss pattern stabilizes.
Assessing Your Hair Transplant Candidacy
The assessment process includes a scalp examination, hair loss classification, medical history review, and discussion of treatment goals and expectations. It’s crucial to have stabilized hair loss before undergoing transplantation to ensure long-term satisfaction with results. Donor hair density and quality significantly impact candidacy, as patients need adequate hair in donor areas to achieve meaningful coverage in recipient zones.
Recovery and Aftercare
Recovery and aftercare are vital components of the hair transplant journey, directly impacting the outcome of the procedure. Proper care during this phase is essential for ensuring the best possible results.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
After the surgery, your scalp may be very tender. You may need to take pain medications for several days. Your surgeon will have you wear bandages over your scalp for at least a day or two. They may also prescribe an antibiotic or an anti-inflammatory drug for you to take for several days.
- Sleep with an elevated head position for the first few nights to minimize swelling.
- Avoid direct pressure on the transplanted area.

Timeline for Recovery
Most people are able to return to work 2-5 days after the operation. Within 2-3 weeks after surgery, the transplanted hair will fall out, but you should start to notice new growth within a few months.
When to Expect Results
Initial growth begins around 3-4 months post-procedure, with significant results visible at 6-9 months, and final results apparent at 12-18 months. Most people will see 60% of new hair growth after 6-9 months.
Long-Term Hair Care After Transplantation
To maintain the health and integrity of your transplanted hair, follow a gentle hair care routine, avoid harsh chemicals, and protect your scalp from sun exposure. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will help monitor progress and address any concerns.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Understanding the potential risks and side effects associated with hair transplant surgery is crucial for informed decision-making. As with any surgical procedure, hair transplants carry certain risks that can impact the outcome and recovery.
Common Temporary Side Effects
Following hair transplant surgery, patients may experience common temporary side effects, including scalp tenderness, swelling, redness, and scabbing. These symptoms typically resolve within 1-2 weeks. It’s essential to follow post-operative care instructions to minimize these effects and ensure proper healing.
- Scalp tenderness and swelling
- Redness and scabbing at the transplant site
- Temporary numbness or tingling sensations
Possible Complications
While rare, potential complications can occur. These include infection, bleeding, scarring, folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles), and cyst formation at the transplant sites. It’s crucial to monitor these complications and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen.
| Complication | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Signs include redness, swelling, fever, and pus | Seek immediate medical attention |
| Bleeding | Excessive bleeding at the transplant site | Contact your surgeon immediately |
| Folliculitis | Inflammation of hair follicles | May require antibiotics |
When to Contact Your Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms after a hair transplant, contact your doctor: heavy bleeding, signs of infection (rash, skin bumps, or cysts), wound incision opening, or swelling in your face accompanied by hives and difficulty breathing (anaphylaxis). Prompt medical attention can prevent serious complications.
By understanding the potential risks and side effects, patients can better prepare themselves for the procedure and recovery. Adhering to post-operative instructions is vital to minimize complications and achieve optimal results.
What to Consider Before Getting a Hair Transplant
Hair transplantation is a significant decision that requires a thorough understanding of the process, costs, and potential outcomes. Before undergoing the procedure, it’s essential to have realistic expectations about the results, understanding that it can improve hair density but may not restore the exact hairline or thickness of youth.
The cost of a hair transplant varies, typically ranging from $4,000 to $15,000, depending on the extent of the procedure, and is rarely covered by insurance as it’s considered cosmetic. Choosing a qualified surgeon who specializes in hair restoration is crucial for successful results.
Potential patients should also consider alternative treatments like medication or PRP therapy before committing to surgery. Understanding the long-term perspective, including the possibility of further hair loss, is vital. A thorough consultation process with multiple specialists can help compare approaches and cost estimates, ensuring an informed decision.
FAQ
What is the success rate of a hair transplant procedure?
The success rate of a hair transplantation procedure is generally high, with most patients experiencing significant hair growth in the recipient area. The success rate depends on various factors, including the surgeon’s expertise, the quality of the donor area, and the patient’s overall health.
Will the transplanted hair look natural?
Yes, when performed by an experienced surgeon, hair transplantation can produce natural-looking results. The grafts are carefully placed to match the patient’s original hair growth pattern, ensuring a seamless blend with the surrounding hair.
Can hair transplantation be used to restore hair on other parts of the body?
While hair transplantation is most commonly used to restore hair on the scalp, it can also be used to restore hair on other areas, such as the eyebrows, beard, or chest. However, the procedure and results may vary depending on the area being treated.
Are there any side effects associated with hair transplantation?
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplantation carries some risks and potential side effects, including swelling, redness, and itching. However, these side effects are typically mild and temporary.
Can I undergo hair transplantation if I have pattern baldness?
Yes, hair transplantation is a popular treatment option for pattern baldness. The procedure involves transplanting hair follicles from the donor area to the balding area, restoring a natural-looking hairline.
Are there any alternative hair restoration techniques available?
Yes, there are alternative hair restoration techniques available, including follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS/FUT). The choice of technique depends on the patient’s individual needs and preferences.
What is the typical recovery time for a hair transplant procedure?
The recovery time for a hair transplant procedure varies depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. Generally, patients can resume their normal activities within a few days to a week after the procedure.