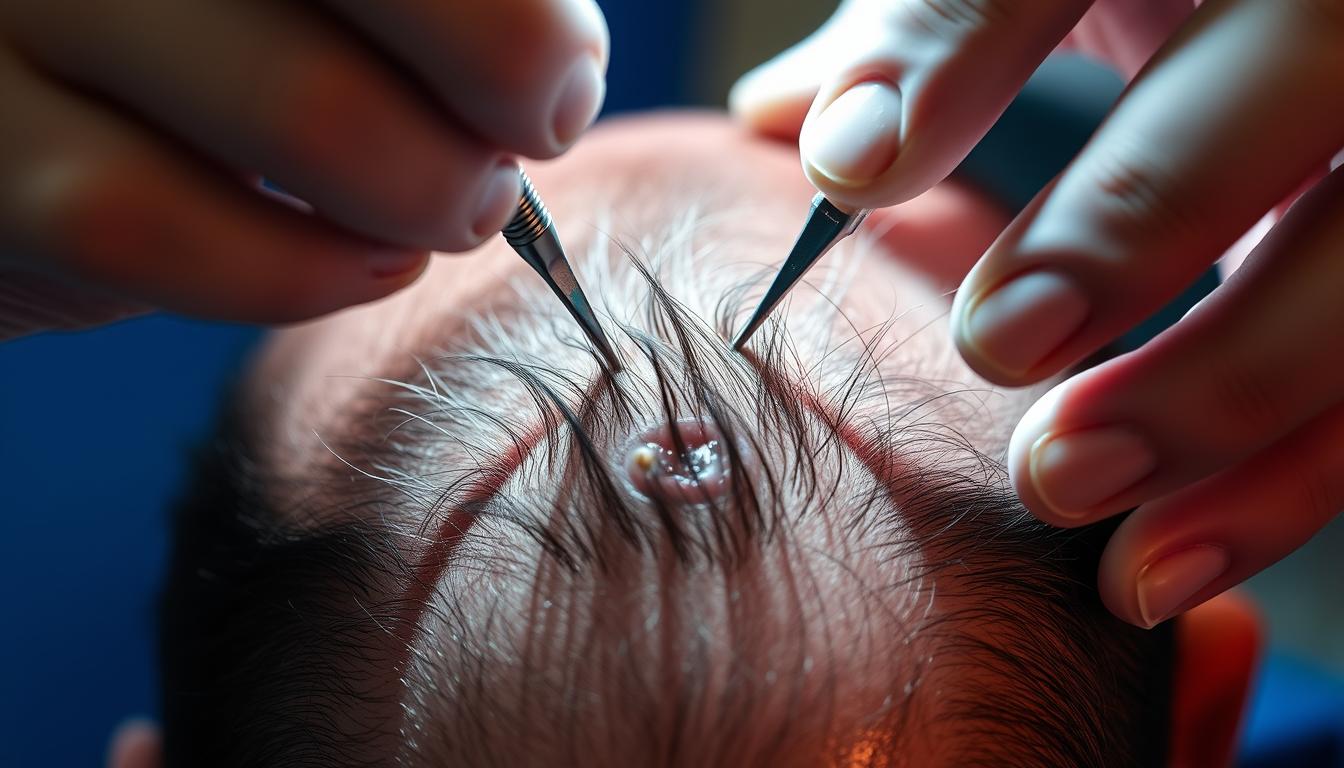
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to restore hair growth in balding or thinning areas of the scalp. This technique has evolved significantly since its introduction in the 1950s, becoming a highly effective solution for permanent hair restoration.
The fundamental principle behind hair transplants involves relocating hair follicles from areas with healthy growth to balding regions, creating a natural-looking hairline. Modern techniques focus on strategically placing individual hair follicles to match the patient’s natural growth pattern.
With hair loss affecting millions of Americans, hair transplant surgery has become an increasingly sought-after solution. Understanding how this procedure works is essential for making an informed decision about whether it’s right for you.
Key Takeaways
- Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that restores hair growth in balding areas.
- The technique involves relocating hair follicles from healthy growth areas to balding regions.
- Modern hair transplant techniques focus on creating a natural-looking hairline.
- Hair loss affects millions, making hair transplants a sought-after solution.
- Understanding the procedure is crucial for making an informed decision.
Understanding Hair Transplantation
Understanding the process of hair transplantation is crucial for those considering this surgical option. Hair transplantation is a complex procedure that involves relocating hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves removing hair follicles from a donor site, typically the back of the head, and implanting them into areas experiencing thinning or baldness. This procedure works on the principle that hair follicles from the back and sides of the scalp are genetically resistant to the hormones that cause hair loss.
Common Causes of Hair Loss
Androgenetic alopecia, or male and female pattern baldness, is the most common cause of hair loss, affecting approximately 50 million men and 30 million women in the United States. Other causes include traction alopecia, scarring from injuries, and certain medical conditions or treatments.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate?
Ideal candidates for hair transplantation have sufficient donor hair, are in good general health, and have realistic expectations. They typically have been experiencing hair loss for several years. A thorough consultation with a qualified hair restoration specialist is essential to determine candidacy.
| Candidate Characteristics | Description |
|---|---|
| Sufficient Donor Hair | Having enough hair to harvest for transplantation |
| Good General Health | Being free from certain medical conditions that could complicate surgery |
| Realistic Expectations | Understanding the potential outcomes and limitations of hair transplantation |
How Does a Hair Transplant Work?
Understanding how a hair transplant works requires knowledge of both the harvesting and implantation stages. Hair transplantation is a sophisticated surgical technique that involves relocating hair follicles from one part of the scalp to another.
The Basic Principles of Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation operates on the principle of “donor dominance,” where hair follicles retain their genetic characteristics even when moved to a new location on the scalp. This principle is fundamental to the success of the procedure.
Donor Areas vs. Recipient Areas
The donor area, typically located at the back and sides of the head, contains hair follicles that are genetically resistant to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for hair loss. During the transplant, individual hair follicular units are extracted from the donor area and implanted into the recipient area, where they establish a new blood supply through revascularization.

The Science Behind Hair Grafting
Modern hair transplant techniques focus on preserving the integrity of each follicular unit to ensure maximum survival rate and natural-looking results. The angle, direction, and distribution of transplanted grafts are meticulously planned to match the patient’s natural hair growth pattern.
| Technique | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS) | A band of hair-covered skin is removed from the lower back of the scalp, and tiny grafts are dissected from this strip. | Allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session. |
| Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) | Individual grafts are directly extracted from the donor site using a micro punch. | Minimally invasive, reducing scarring and recovery time. |
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures
When it comes to hair transplantation, understanding the different procedures available is crucial for making an informed decision. Hair transplant surgery has evolved, offering various techniques to address hair loss effectively.
Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS)
FUSS involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and then implanting these units into the recipient area. This procedure typically allows for harvesting a larger number of grafts in a single session.
Procedure Steps
- The surgeon removes a 6- to 10-inch strip of skin from the back of the head.
- The strip is then divided into 500 to 2,000 tiny grafts, each containing an individual hair or a few hairs.
- The scalp is then closed, leaving a linear scar.
Advantages and Disadvantages
FUSS is efficient for covering extensive balding areas but leaves a linear scar, which can be concealed by surrounding hair. However, this scar may be visible with very short hairstyles.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE involves individually extracting follicular units directly from the donor area using a micro-punch tool, leaving tiny dot-like scars instead of a linear scar.
Procedure Steps
- A section of the back of the scalp is shaved.
- Hair follicles are removed one by one from the donor area.
- The area heals with small dots, which are usually concealed by existing hair.
Advantages and Disadvantages
FUE allows for greater flexibility in harvesting hair from various body areas and is ideal for patients who prefer to wear their hair very short. However, it tends to be more expensive and time-consuming than FUSS.
FUSS vs. FUE: Which Is Right for You?
When choosing between FUSS and FUE, patients should consider factors such as the extent of hair loss, desired hairstyle, budget constraints, recovery time preferences, and the surgeon’s recommendation. Both procedures have high success rates when performed by experienced surgeons.
The Hair Transplant Procedure: Step by Step
The hair transplant procedure is a detailed process that involves harvesting, creating recipient sites, and implanting hair grafts. This surgical treatment is designed to restore a natural-looking hairline for individuals experiencing hair loss.
Pre-Procedure Preparation
Before the hair transplant surgery, patients undergo a thorough consultation with their surgeon to evaluate their hair loss pattern and discuss expectations. The surgeon designs a customized treatment plan, advises on medications to avoid, and marks the recipient areas and hairline on the day of the procedure.
Harvesting the Hair Grafts
During the harvesting phase, the surgeon extracts grafts from the donor area using either the FUSS or FUE technique. Each graft contains 1-4 hair follicles, which are carefully preserved to ensure successful transplantation.

Creating Recipient Sites
The creation of recipient sites is a critical step where the surgeon makes tiny incisions in the balding areas, controlling the angle, direction, and distribution of future hair growth.
Implanting the Hair Grafts
During implantation, each graft is precisely placed into the pre-made incisions. Finer single-hair grafts are positioned along the hairline for a natural appearance, while multi-hair grafts are placed behind for density.
| Procedure Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Procedure Preparation | Consultation, medication advice, and marking recipient areas | Customized treatment plan, avoiding certain medications |
| Harvesting Hair Grafts | Extracting grafts from the donor area using FUSS or FUE | Preserving graft integrity, minimizing donor site impact |
| Creating Recipient Sites | Making tiny incisions in balding areas | Controlling angle, direction, and distribution for natural hair growth |
| Implanting Hair Grafts | Placing grafts into pre-made incisions | Ensuring natural appearance and density |
The entire procedure typically takes 4-8 hours, depending on the number of grafts being transplanted. Larger cases may be split into multiple sessions to ensure optimal results.
Advanced Hair Restoration Techniques
Innovative methods in hair restoration are changing the way we tackle baldness. Advanced techniques offer new solutions for individuals experiencing hair loss, providing more options beyond traditional transplants.
Tissue Expansion Technique
Tissue expansion is a procedure that involves inserting a balloon-like device under the hair-bearing scalp near a bald area. This device is gradually inflated over several weeks, causing the skin to expand and grow new cells.
Flap Surgery Method
Flap surgery involves removing a section of bald scalp and replacing it with a flap of hair-bearing skin. This technique can cover large areas of baldness quickly and is customized to each patient’s needs.
Scalp Reduction Procedure
Scalp reduction involves removing bald scalp areas and pulling the surrounding hair-bearing skin together. The pattern of scalp removal varies based on the extent of coverage needed.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue Expansion | Balloon-like device inserted under scalp to expand skin | Significant coverage in a short time |
| Flap Surgery | Replacing bald scalp with hair-bearing skin flap | Quick coverage of large bald areas |
| Scalp Reduction | Removing bald scalp and pulling hair-bearing skin together | Effective for top and back of the head |
Recovery and Aftercare
The recovery process is a crucial aspect of a hair transplant, requiring careful attention to aftercare instructions. A successful hair transplant is contingent upon not just the procedure, but also the post-operative care.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Immediately after a hair transplant procedure, patients can expect some tenderness, swelling, and mild discomfort in both the donor and recipient areas of the scalp. The surgeon typically applies bandages to the scalp for 1-2 days and may prescribe antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications to prevent infection and reduce swelling.
Timeline for Recovery
Most patients can return to work and normal activities within 2-5 days after the procedure, though strenuous exercise and activities that might cause sweating should be avoided for at least two weeks. Between 2-3 weeks post-procedure, patients experience “shock loss” where the transplanted hair falls out—this is a normal part of the process.
Managing Discomfort and Side Effects
Potential side effects during recovery include temporary numbness, itching, and swelling that may move down to the forehead and around the eyes. Patients should follow the surgeon‘s specific instructions for washing the hair and scalp to manage these side effects.
When to Return to Normal Activities
The timeline for new hair growth begins around 3-4 months after the procedure, with most patients seeing approximately 60% of the final results by 6-9 months. Full results from a hair transplant typically take 12-18 months to manifest.
By following the surgeon‘s care instructions and being patient, individuals can achieve the best possible outcome from their hair transplant.
Results and Expectations
Understanding the outcomes of a hair transplant is crucial for managing expectations. The procedure is designed to provide a natural-looking hairline and restore hair growth in balding areas.
Hair Growth Timeline
The hair growth timeline after a transplant follows a predictable pattern. Initially, the transplanted hair falls out within 2-3 weeks, a phenomenon known as shock loss. However, new growth begins around 3-4 months, and significant results become visible at 6-9 months. Full maturation of transplanted hair follicles takes 12-18 months.
Long-Term Results and Success Rates
Hair transplants are designed to be permanent, with the transplanted hair continuing to grow naturally throughout a patient’s lifetime. Modern hair transplant procedures have high success rates, with approximately 85-95% of transplanted grafts surviving and growing in their new location when performed by experienced surgeons.
Potential Complications
While generally safe, hair transplants carry some risks, including infection, bleeding, scarring, and folliculitis. Some patients may experience temporary or permanent numbness in the treated areas, though sensation typically returns within a few months.
The quality of results depends significantly on the surgeon’s skill and experience, the patient’s hair characteristics, and the availability of sufficient donor hair. Most patients report high satisfaction rates with their hair transplant results, with studies showing improved self-confidence and quality of life following successful procedures.
Making an Informed Decision About Hair Transplantation
To make an informed decision about hair transplantation, several key factors must be considered. Patients should research thoroughly and have realistic expectations.
Consulting with board-certified specialists who have extensive experience in hair restoration is crucial. Factors such as the extent of hair loss, overall health, and financial investment should be evaluated.
The cost of hair transplants in the United States can range from $4,000 to $15,000. Understanding the full financial commitment and potential results is essential.
FAQ
What is the typical recovery time for a hair restoration procedure?
Most people can return to their normal activities within 7-10 days after the procedure. However, it may take several weeks for the scalp to fully recover.
Will the transplanted hair fall out after the procedure?
Initially, the transplanted hairs may shed, but this is a normal part of the process. The hair follicles will then start to produce new hair growth.
Can hair transplantation be used to restore hair loss in other areas of the body?
While hair transplantation is most commonly used to restore hair on the scalp, it can also be used to restore hair in other areas, such as the eyebrows or beard.
What are the potential risks and complications of hair restoration surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks and potential complications, including infection, scarring, and graft failure. However, these risks can be minimized by choosing a qualified and experienced surgeon.
How long does it take to see the final results of hair transplantation?
It can take several months to a year or more to see the full results of hair transplantation, as the hair growth process is gradual.
Can I undergo hair transplantation if I have thinning hair?
Yes, hair transplantation can be used to restore hair in areas with thinning hair. However, the success of the procedure will depend on the extent of hair loss and the quality of the donor hair.