A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair from one part of the head to another. This procedure is typically performed to address hair loss and restore a natural-looking hairline.
The process involves relocating healthy hair follicles from the back or sides of the head to areas experiencing thinning or baldness. By doing so, it provides a permanent solution for individuals experiencing hair loss due to pattern baldness or other forms of alopecia.
Key Takeaways
- A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that restores hair growth.
- It provides a permanent solution for hair loss.
- The procedure involves relocating healthy hair follicles.
- Hair transplants are typically performed under local anesthesia.
- The result is a natural-looking hairline.
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Causes
Understanding the root causes of hair loss is crucial for determining the most effective treatment. Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can result from a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and lifestyle influences.
Common Types of Hair Loss
Hair loss can manifest in different forms, each with distinct characteristics. The most common types include androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, and traction alopecia. Androgenetic alopecia is the most prevalent form, influenced by genetics and hormonal factors.
A comprehensive understanding of these conditions is essential for identifying the underlying cause of an individual’s hair loss.
| Type of Hair Loss | Causes | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Androgenetic Alopecia | Genetics, Hormonal Influence | Pattern baldness in men and women |
| Alopecia Areata | Autoimmune Disorder | Patchy hair loss |
| Telogen Effluvium | Stress, Hormonal Changes | Temporary hair loss after stress or hormonal shifts |
| Traction Alopecia | Hair styling practices | Hair loss due to constant pulling on hair follicles |
Pattern Baldness and Genetics
Pattern baldness, or androgenetic alopecia, is largely influenced by genetic factors. The role of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in pattern baldness is significant, as it affects the hair growth cycle by shortening the anagen phase and leading to thinner, shorter hairs.
Understanding the genetic predisposition to pattern baldness can help individuals anticipate and potentially mitigate its effects through early intervention.
What Is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical technique that relocates hair follicles from one part of the head to another. This procedure involves moving hair from the back or sides of the head, known as donor areas, to the front or top, which are typically experiencing thinning or baldness.
The Science Behind Hair Transplantation
The success of hair transplantation is rooted in the principle of “donor dominance.” This concept explains why transplanted hair continues to grow in its new location, unaffected by the factors that caused the original hair loss. The transplanted follicles are resistant to the hormones responsible for pattern baldness, ensuring a natural and lasting result.
Hair Transplant as a Permanent Solution
A hair transplant offers a permanent solution for hair loss. The transplanted hair follicles are not only resistant to balding but also grow naturally, creating a dense and natural-looking hairline. Modern hair transplantation techniques have evolved to produce results that are virtually indistinguishable from natural hair growth. Key benefits include:
- Long-lasting results due to the resistance of transplanted follicles to balding hormones
- Natural appearance achieved through meticulous graft placement and density planning
- Minimally invasive procedure with significant aesthetic improvement
By understanding the science behind hair transplantation and its potential as a permanent solution, individuals can make informed decisions about their hair restoration options.
Types of Hair Transplant Procedures
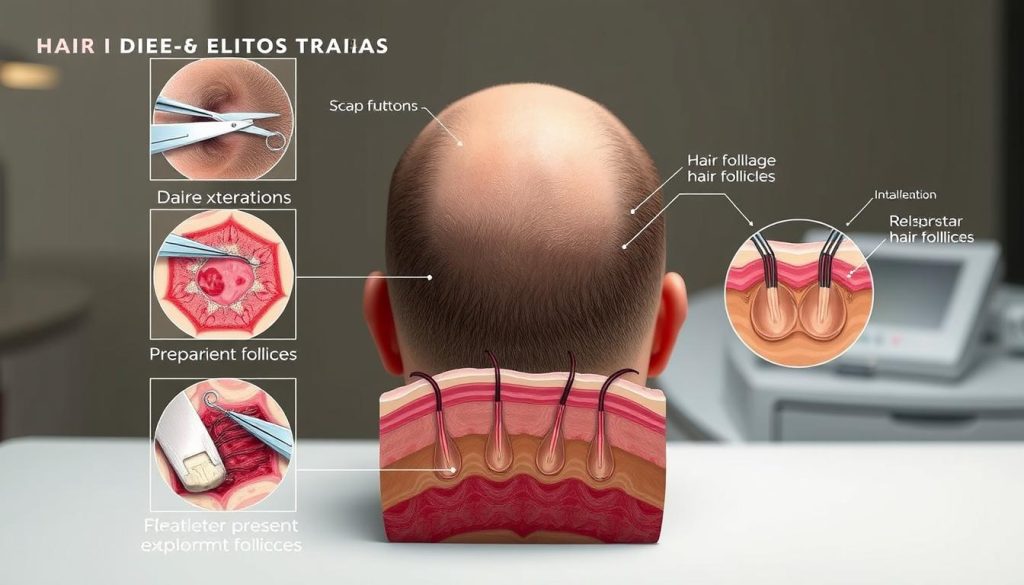
There are primarily two techniques used in hair transplantation: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). These procedures have revolutionized the treatment of hair loss, offering patients effective solutions to restore their hair.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
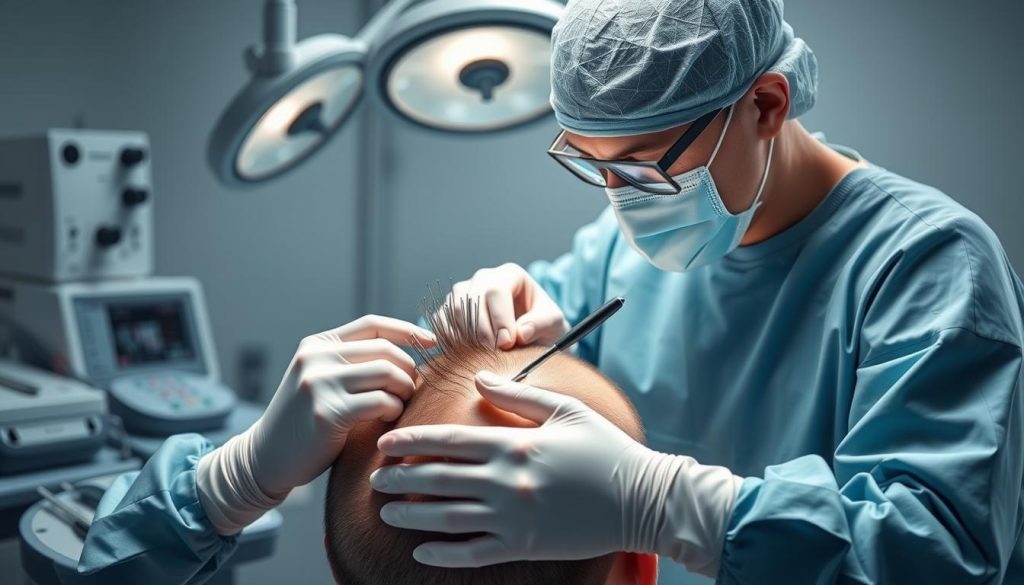
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as the strip method, involves harvesting a strip of tissue from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units under microscopes, and then transplanting these grafts into the recipient area. This technique allows for the transplantation of a large number of hair follicles in a single session.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a technique where individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using specialized micro-punches, eliminating the need for a linear incision. This method results in less scarring and a quicker recovery compared to FUT. FUE is particularly preferred for its minimally invasive nature and the ability to extract grafts from various parts of the body.
Both FUT and FUE have their advantages and are chosen based on factors such as the extent of hair loss, donor hair availability, scarring concerns, and recovery preferences. Newer variations like robotic FUE, sapphire FUE, and DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) offer increased precision and potentially better outcomes, further expanding the possibilities in hair transplant procedures.
Are You a Good Candidate for Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant can be an effective solution for hair loss, but it’s essential to evaluate your candidacy based on several factors. The procedure is not suitable for everyone, and understanding your eligibility is crucial before proceeding.
Ideal Candidates for the Procedure
Ideal candidates for a hair transplant include individuals with stable hair loss patterns, sufficient donor hair density, and realistic expectations about the results. Men with male pattern baldness, women with thinning hair, and those who have lost hair due to injury or burns are typically considered good candidates. Age is also a consideration, as younger patients with progressive hair loss might be advised to wait or combine transplantation with medical treatments.
When Hair Transplant May Not Be Suitable
A hair transplant may not be the best option for individuals with certain conditions. For instance, women with a widespread pattern of hair loss throughout the scalp or those who don’t have enough donor hair sites may not be suitable candidates. Additionally, people who form keloid scars or are experiencing hair loss due to medication like chemotherapy may also not be ideal candidates.
| Candidate Characteristics | Ideal | Not Ideal |
|---|---|---|
| Hair Loss Pattern | Stable, localized | Widespread, diffuse |
| Donor Hair Availability | Sufficient | Insufficient |
| Health Status | Good overall health | Certain medical conditions or undergoing chemotherapy |
As noted by a hair restoration expert, “Assessing a patient’s suitability for a hair transplant requires a comprehensive evaluation of their hair loss condition, donor hair availability, and overall health status.” A professional consultation is necessary to determine your candidacy and discuss what you can expect from the procedure.
The Hair Transplant Process Explained
Individuals contemplating a hair transplant should be aware of the steps involved in the process. A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that requires careful planning and execution.
Before the Procedure: Preparation Steps
Before undergoing a hair transplant, patients must prepare by avoiding certain medications, making lifestyle adjustments such as smoking cessation and limiting alcohol, and following specific instructions for the day before and morning of the surgery.
During the Procedure: What Happens
During the procedure, the surgeon cleans the scalp and numbs an area of the head with local anesthesia. Tiny holes are made in the recipient area of the scalp, and hairs are gently placed in these holes. A single session can involve transplanting hundreds or thousands of hairs, taking around 4 hours or more.
Anesthesia and Pain Management
Local anesthesia with sedation is typically used during hair transplant surgery. Surgeons ensure patient comfort throughout the procedure by carefully managing anesthesia and pain.
Recovery and Aftercare Following a Hair Transplant
After undergoing a hair transplant, proper care is crucial for optimal recovery. The scalp may be sore, and patients may need to take medications following surgery, such as pain medication, antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection, and anti-inflammatory medications to minimize swelling.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Immediate post-procedure care is vital for the success of the hair transplant. Patients are advised on how to sleep, wash their scalp, manage discomfort, and protect the newly transplanted grafts during the first week after surgery. Most people can return to work within several days after the procedure.
- Keep the scalp clean to prevent infection
- Avoid strenuous activities for a few days to weeks
- Follow the medication protocol as prescribed
Long-term Maintenance
For long-term success, it’s essential to maintain the health of both the transplanted hair and the existing hair. This may involve using hair loss medications like finasteride or minoxidil to protect non-transplanted hair. Regular check-ups with the surgeon are also recommended to monitor progress over several weeks and beyond.
| Care Aspect | Immediate Post-Procedure | Long-term |
|---|---|---|
| Scalp Care | Gentle washing, avoid direct water pressure | Regular washing, possibly with hair loss medications |
| Activity Level | Avoid strenuous activities | Resume normal activities gradually |
| Medication | Follow prescribed pain and antibiotic medication | May include hair loss prevention medications |
Timeline of Results: What to Expect
Understanding the timeline of results after a hair transplant is crucial for managing expectations. The process involves several stages, from the initial shedding phase to the final growth of new hair.
The Shedding Phase
It’s typical for the transplanted hair to fall out 2 to 3 weeks after the procedure. This shedding phase is a normal part of the process and makes way for new hair growth. Patients should be prepared for this temporary loss, which usually occurs within 2-4 weeks post-procedure.
New Growth and Final Results
Most people will see some new hair growth 8 to 12 months after surgery. The growth phases progress from fine hairs appearing around months 3-4 to the thickening and maturation of hair between months 6-12. The full aesthetic outcome, including density and texture matching, may take 12-18 months to achieve.
| Months Post-Procedure | Expected Progress |
|---|---|
| 2-4 weeks | Shedding of transplanted hair |
| 3-4 months | Initial fine hairs appear |
| 6-12 months | Progressive thickening and maturation of hair |
| 12-18 months | Full aesthetic outcome achieved |
Potential Risks and Complications
Understanding the potential risks and complications associated with hair transplant surgery is essential for informed decision-making. While generally considered safe, hair transplant procedures can have side effects.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects are typically minor and temporary, including swelling of the scalp, bruising around the eyes, and numbness or lack of sensation on the treated areas of the scalp. Patients may also experience itching, inflammation, or infection of the hair follicles.
Serious Complications and How to Avoid Them
More serious complications, although rare, can include excessive bleeding, infection, and scarring. To minimize risks, it’s crucial to choose an experienced surgeon and follow pre-operative and post-operative instructions carefully. A well-structured surgery plan and proper aftercare can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
| Complication | Description | Prevention/Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Infection | Bacterial infection of the scalp | Antibiotics, proper wound care |
| Excessive Bleeding | Heavy bleeding during or after surgery | Careful patient selection, controlled surgery |
| Scarring | Visible scars on the scalp | Experienced surgeon, proper technique |
Cost Considerations for Hair Transplant Surgery
The cost of hair transplant surgery varies widely based on several key factors. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals considering this procedure to manage their expectations and make informed decisions.
Factors Affecting Hair Transplant Pricing
The cost of hair transplant surgery can range from $4,000 to $15,000 or more, with the national average being around $7,000 for a standard procedure. Several factors influence this cost, including the technique used (FUT vs. FUE), the number of grafts required, the surgeon’s experience and reputation, geographic location, and facility fees.
The technique used significantly impacts the cost. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is generally more expensive than Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) due to its labor-intensive nature. The number of grafts required also affects the overall cost, with larger areas of coverage resulting in higher costs but often lower per-graft rates due to economies of scale.
Insurance Coverage and Financing Options
Hair transplants are typically considered cosmetic procedures and are not covered by most health insurance plans. However, there are rare exceptions for reconstructive cases following injury or disease. Patients should check with their insurance providers to determine the extent of their coverage.
For those who need financial assistance, various financing options are available, including medical financing companies, payment plans offered by clinics, health savings accounts (HSAs), and personal loans. These options can make the investment in hair transplant surgery more manageable.
Alternatives to Hair Transplant Surgery
Beyond surgical hair transplants, several non-invasive and pharmacological treatments can address hair loss. These alternatives offer individuals a range of options to manage hair loss effectively.
Medication Options
Medications such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and finasteride (Propecia) are commonly prescribed to improve hair regrowth and slow down hair loss. Minoxidil is applied topically to stimulate hair growth, while finasteride is taken orally to block the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with hair loss.
Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Methods
Non-surgical hair restoration includes treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy, low-level laser therapy (LLLT), and microneedling. These methods aim to stimulate hair growth and improve the density of existing hair. Additionally, cosmetic alternatives such as scalp micropigmentation and hair fibers can provide immediate aesthetic improvement.
Is a Hair Transplant Worth It? Making Your Decision
Deciding on a hair transplant requires careful consideration of several key factors. Individuals should weigh the potential benefits against the costs and risks. For those who haven’t found success with treatments like minoxidil or Rogaine, hair transplantation can be a viable option. It’s crucial to select a qualified surgeon and have realistic expectations about results. By understanding the process and its implications, individuals can make an informed decision about whether a hair transplant is right for them.
FAQ
What is the ideal age for undergoing a hair restoration procedure?
The ideal age for a hair restoration procedure varies, but it’s typically recommended for individuals with stabilized pattern baldness. Most surgeons suggest waiting until the baldness pattern has fully developed, usually in the late 20s to early 30s.
How long does it take to recover from scalp surgery?
Recovery from scalp surgery typically takes around 7-10 days, during which time patients may need to take time off work. The donor area may be sore, and grafts may be sensitive, but these symptoms usually subside within a few days.
Are hair transplants permanent?
Yes, hair transplants are considered a permanent solution for hair loss. The transplanted follicles are resistant to pattern baldness and will continue to grow naturally.
Can alopecia be treated with hair restoration?
Yes, alopecia can be treated with hair restoration in some cases. However, the success of the procedure depends on the type and extent of alopecia. It’s essential to consult with a qualified surgeon to determine the best course of treatment.
How many grafts are needed for a full scalp coverage?
The number of grafts needed for a full scalp coverage varies depending on the extent of hair loss and the desired density. On average, a full scalp coverage may require anywhere from 2,000 to 5,000 grafts.
Are there any non-surgical alternatives to hair restoration?
Yes, there are non-surgical alternatives to hair restoration, including medication options like Minoxidil and Finasteride, as well as non-surgical hair restoration methods like low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy.
How much does hair restoration surgery cost?
The cost of hair restoration surgery varies depending on factors like the location, surgeon’s fees, and the number of grafts required. On average, the cost can range from ,000 to ,000 or more.
Can I return to work after scalp surgery?
Most patients can return to work within 7-10 days after scalp surgery. However, it’s essential to follow the surgeon’s instructions and take necessary precautions to ensure a smooth recovery.
